10.4 Linux 上最优雅的命令调用方式:sh¶

在编写 Python 脚本的时候,很经常需要我们去调用系统的命令,方法有很多种,比如 os.popen,os.system,commands,还有 subprocess。
今天明哥要介绍一种更加优雅的方法,就是 sh
这个第三方库,它能让你像调用方法那样去调用系统中的命令。
使用前,当然是安装它,sh 支持 Python 2 也支持 Python3,这里以
Python 3 为例。
$ python3 -m pip install sh
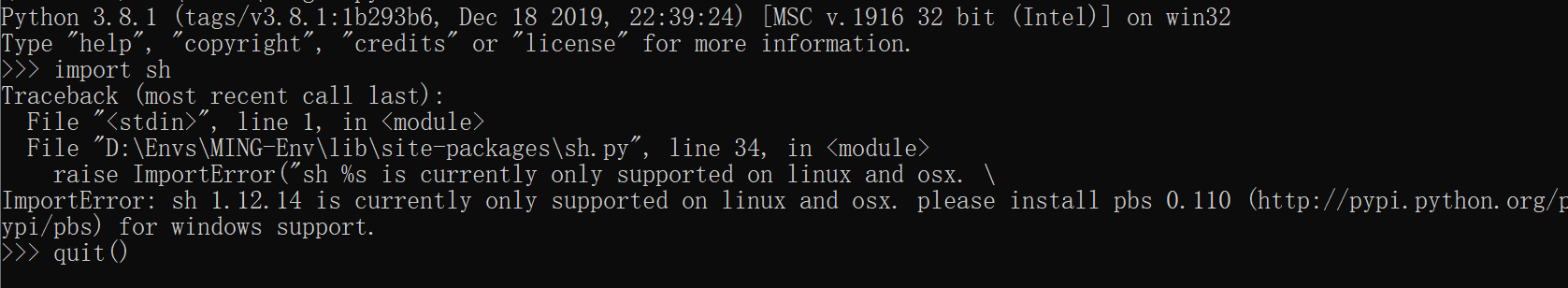
这里要注意一点,虽然在 Windows
上也可以安装成功,但是并不能使用,如果你尝试在 Windows 导入
它,会友好地提示你,该库只适用于 Linux 及 OSX 系统,假如你也想要在
Windows 使用,它推荐你使用它的 兄弟库 - pbs
(https://pypi.org/project/pbs/)。
安装完成后,就可以直接使用它了,以下几个示例,非常简单,简单到我感觉只要 demo ,而不需要任何的中文解释就可以让你知道他是如何使用的。
1. 列出目录文件¶
使用 ls
>>> import sh
>>> sh.ls("/home", "-l", color="never")
total 4
drwx------ 3 centos centos 4096 Mar 8 2019 centos
使用 glob
>>> sh.glob("/etc/*.conf")
['/etc/mke2fs.conf', '/etc/dnsmasq.conf', '/etc/asound.conf']
调用程序¶
>>> import sh
>>> r=sh.Command('/root/test.py')
>>> r()
hello,world
上面我们的 ls ,也可以通过这种方式执行,只是不能再加参数了。
sh.Command("ls")()
管道¶
>>> print(sh.sort(sh.du(sh.glob('*'),'-shc'),'-rn'))
712K distribute-0.6.49.tar.gz
672K setuptools-1.1.5.tar.gz
548K get-pip.py
管道是有序的,默认由内而外,但如果需要并行呢?加个_piped=True
>>> for line in sh.tr(sh.tail("-f", "/home/mysql/mysql/log/alert.log", _piped=True), "[:upper:]", "[:lower:]", _iter=True):
... print line
...
innodb: doublewrite buffer not found: creating new
innodb: doublewrite buffer created
innodb: 127 rollback segment(s) active.
innodb: creating foreign key constraint system tables
innodb: foreign key constraint system tables created
